- Posted on
- Bhanu Pratap
SAP MM (Materials Management) is a module in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that provides companies with materials, inventory, and warehouse management capabilities. The primary goal of SAP MM software is to make sure that materials are always kept in proper quantities and without shortages or gaps in the organisation’s supply chain. It also helps supply chain professionals and other SAP users complete the purchasing of goods in a timely and cost-effective way and be able to deal with day-to-day changes in these processes.
One of the critical modules in SAP ECC, SAP MM, is part of SAP ECC’s logistics function and plays a vital role in a manufacturer’s supply chain. It integrates with other ECC components like Production Planning (PP), Sales and Distribution (SD), Plant Maintenance (PM), Quality Management (QM), Finance and Controlling (FICO), and Human Capital Management (HCM).
Support for SAP ECC is scheduled to stop in 2025, at which point it will be replaced by SAP S4 HANA MM. It’s not clear from SAP how the functions of MM will transition to S4 HANA, although the newer platform has components to address the core issues behind material management in SAP. SAP solutions include ease of ERP and this blog will help you understand SAP MM and its modern usage.
Features of SAP MM (Materials Management):
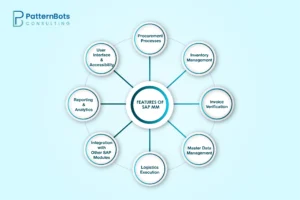
Material management in SAP is a complete module designed for efficient procurement, inventory management, and materials handling in an organisation. Here are the main features of SAP MM:
1. Procurement Processes:
- Purchase Requisition (PR): Users can start the procurement process by requesting materials or services.
- Request for Quotation (RFQ): The organisation can invite prices from potential suppliers.
- Purchase Order (PO): Users create purchase orders that detail the terms, conditions, and quantities for materials or services.
2. Inventory Management:
- Goods Receipt (GR): This records the arrival of materials into inventory and updates stock levels.
- Goods Issue (GI): This documents the removal of materials from inventory for production or consumption.
3. Invoice Verification:
- Three-Way Match: This checks invoices against purchase orders and goods receipts to ensure accuracy before payment.
- Vendor Invoice Management (VIM): This tool helps automate and streamline the accounts payable process.
4. Master Data Management:
- Material Master: This is a central database containing detailed information about materials, including purchasing, sales, and inventory data.
- Vendor Master: This keeps information about suppliers and vendors to support efficient procurement.
5. Logistics Execution:
- Warehouse Management (WM): This connects with SAP WM for improved warehouse handling and efficiency.
- Handling Unit Management (HUM): This tracks packaging materials during logistics operations.
6. Integration with Other SAP Modules:
- Integration with SAP SD (Sales and Distribution): This ensures smooth cooperation between procurement and sales processes.
- Integration with SAP PP (Production Planning): This supports the planning and execution of production activities.
7. Reporting and Analytics:
- SAP Analytics: This offers various reporting tools and analytics to monitor and analyse procurement, inventory, and materials data in real-time.
8. User Interface and Accessibility:
- SAP Fiori: This provides a modern and user-friendly interface for better user experience and accessibility.
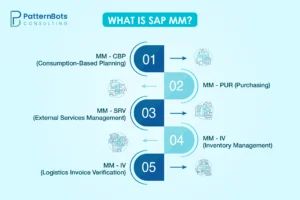
Components of SAP MM
The SAP MM software includes several components that work together. This integration allows different departments to share information easily and update data in real time. SAP MM has five main components, each with its own sub-modules. Here are the five key components:
1. MM – CBP (Consumption-Based Planning)
This component uses past consumption data to predict future needs through statistical methods. Its main job is to monitor stock levels and automatically create procurement proposals for production and purchasing when a stock falls below a set point or based on past usage.
2. MM – PUR (Purchasing)
The purchasing component facilitates smooth communication among everyone involved in the procurement process. Its main tasks include:
- Managing the purchase of materials and services
- Monitoring vendor deliveries
- Tracking payments to vendors
- Finding potential suppliers for needs
3. MM – SRV (External Services Management)
This component helps manage external services. It supports two types of services:
- Planned services: Where the requirements are known at the start
- Unplanned services: Where the requirements are unclear and procurement depends on a budget limit.
4. MM – IV (Inventory Management)
This component manages material stocks in both quantity and value. It includes tasks like:
- Keeping track of physical inventory
- Documenting the movement of goods
5. MM – IV (Logistics Invoice Verification)
This component verifies incoming invoices at the end of the logistics supply chain. It checks prices, content, and quantity of invoices once a vendor sends them. It then adds the information to the system and forwards it to financial accounting and other materials management functions.
Types of procurements in SAP MM
Basic procurement
Basic procurement is the process of buying goods or services in the right amount, at the right price, and at the right time. It’s essential to find a balance between quantity, price, and timing.
For example, organisations try to keep inventory levels low because high inventory can be expensive. However, running out of raw materials can halt production, which is also a problem.
Getting the lowest price for a product or service is often important. Still, it’s equally crucial to balance product availability, quality, and relationships with vendors.
Procurement lifecycle for basic SAP MM module
Procurement usually follows a series of steps in modern organisations. Here’s how it works:
1. Requirement and Information Gathering
The process starts by identifying what products and how much of them are needed. Next, it is important to find suppliers that can meet these needs.
2. Supplier Contact
After figuring out the requirements, you look for suppliers who can provide the products or services. You then send out requests for quotes or reach out to suppliers directly.
3. Background Review
Once you identify potential suppliers, you check the quality of their products or services. It’s also important to look into any additional services they offer, like installation, warranties, and maintenance. You can request some samples to test the quality.
4. Negotiation
You negotiate with suppliers about the price, availability, and delivery timelines for the products or services. After negotiations, you sign a contract, which is a legal document that outlines essential details like price, quantity, and delivery date.
5. Order Fulfillment
The supplier ships the ordered products to you, and you make the payment. The process may also include training or installation services.
6. Consumption, Maintenance, and Disposal
As you use the products or services, you evaluate their performance and assess any ongoing support you may need.
7. Contract Renewal
Once the products or services are used up or the contract ends, you decide whether to renew the contract or reorder. You review your experience with the suppliers and decide if you want to continue with them or look for new options.
Special procurement
Special stocks are managed differently because they don’t belong to the company. They are stored in specific locations. Special procurement and special stock types are grouped into several categories:
1. Consignment Stocks:
These are materials stored at our location but still owned by the vendor. If we use materials from consignment stocks, we must pay the vendor.
2. Third-party Processing:
In this case, a company gives a sales order to an external vendor who directly sends the goods to the customer. The vendor processes the sales order, not the company. We can include third-party items in purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and sales orders.
3. Pipeline Handling:
The company does not need to order or store materials because they come through a pipeline (like oil or water) or other means (such as electricity). The company pays the vendor regularly for the materials consumed.
4. Returnable Transport Stock:
The company orders goods from a vendor, which delivers them in returnable packaging (like pallets or containers). This packaging belongs to the vendor and stays at the customer’s location until it is returned.
5. Subcontracting:
The vendor (subcontractor) receives components from the company to produce a product. The company orders this product through a purchase order. The components needed by the vendor to make the product are listed in the purchase order.
6. Stock Transfer Using Stock Transport Order:
Goods are moved within a company when one plant orders from another plant. This order is made using a special type of purchase order called a stock transport order. This allows the company to request and track the transfer of goods.
Benefits of SAP MM (Material Management)
Companies need to respond quickly to changing client needs and expectations. To deliver products effectively, they must have the right amount of stock available at the right time. A good material management process helps improve the efficiency of the supply chain. SAP MM automates material management and procurement, making them more effective. Here are the key benefits of SAP MM:
- Improves inventory control
- Reduces the risk of excess stock
- Makes inventory maintenance less time-consuming and labour-intensive
- Cuts waste by avoiding outdated or unnecessary items
- Lowers labour costs and maximises employee productivity
- Shortens production cycle times
- Saves costs by reducing the need for storing unwanted items
- Speeds up product delivery
- Enhances transparency in inventory management
- Offers a variety of career opportunities with SAP MM certification.
How we help in SAP MM in consulting?
At PatternBots, we simplify SAP MM processes to improve procurement, inventory management, and supply chain efficiency. We handle everything from implementation and automation to transitioning to SAP S4 HANA MM and providing real-time analytics. Our solutions are cost-effective and future-ready. With expert advice, personalised integrations, and ongoing support, we help businesses make the most of SAP MM for better operations. Work with us to enhance your SAP MM experience.
Frequently Asked Question
SAP Materials Management (SAP MM) is an important part of SAP ERP that helps businesses manage buying, inventory, and supply chain activities effectively. It keeps stock at the right levels, reduces shortages, and simplifies purchasing to lower costs and improve efficiency. If your business involves materials, purchasing, or logistics, SAP MM helps ensure smooth operations and better control over your supply chain.
SAP MM improves purchasing by automating and streamlining purchase requests, managing suppliers, and verifying invoices. It helps track goods accurately, shortens procurement times, and connects easily with finance and inventory systems. With real-time data, businesses can make better decisions, negotiate improved terms with suppliers, and eliminate delays in the supply chain.
SAP MM offers a comprehensive set of features, including:
- Procurement Management: Automates purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and supplier evaluation.
- Inventory Management: Tracks goods receipt, issue, and stock transfers in real time.
- Invoice Verification: Ensures accurate payments through a three-way match of invoices, POs, and goods receipts.
- Master Data Management: Centralised records for materials, vendors, and pricing.
- Integration with Logistics and Warehouse Management: Enhances supply chain visibility and efficiency.
- Reporting & Analytics: Provides real-time insights to optimise procurement and inventory control.
Yes, SAP MM integrates seamlessly with various SAP modules, ensuring a unified approach to enterprise resource planning. Key integrations include:
- SAP SD (Sales & Distribution): Aligns procurement with customer orders.
- SAP PP (Production Planning): Ensures timely material availability for manufacturing.
- SAP FICO (Finance & Controlling): Links procurement with financial accounting.
- SAP WM (Warehouse Management): Enhances inventory tracking and logistics.
- SAP QM (Quality Management): Ensures quality control for incoming materials.
At PatternBots, we provide end-to-end SAP MM consulting and implementation services, ensuring a seamless transition to an optimised procurement and inventory management system. Our approach includes:
- Process Assessment & Strategy: Analysing your current supply chain and designing a tailored SAP MM solution.
- Seamless Implementation: Configuring and integrating SAP MM modules to align with your business needs.
- Training & Support: Empowering your team with hands-on training and ongoing assistance.
- SAP S4 HANA Transition: Ensuring a smooth migration from SAP ECC to S4 HANA with minimal disruption.